Looking for Brachial Plexus Injury treatment in Gurgaon, India? Consult Dr. Pradeep Kumar Singh, an expert plastic surgeon with 17+ years of experience in nerve repair.
Brachial Plexus Injury Treatment by Dr. Pradeep Kumar Singh
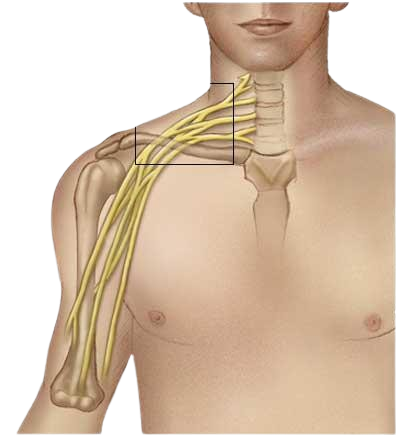
The brachial plexus is a group of nerves connecting the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm, and hand. These nerves are responsible for movement, sensation, and muscle control in the upper limb.
When these nerves are injured due to trauma, accidents, birth complications, or medical conditions, it can lead to weakness, loss of movement, pain, or even complete paralysis of the arm. This condition is known as a Brachial Plexus Injury and requires timely specialist care for the best recovery.
At Dr. Pradeep Kumar Singh’s neurosurgical practice, we focus on precise diagnosis, advanced nerve repair, and reconstruction surgeries tailored to the severity of the injury. Our approach includes both surgical expertise and structured rehabilitation to help restore strength, function, and sensation.
We are committed to improving mobility, reducing pain, and helping patients regain confidence in daily activities.
Contact With us Today
What is Brachial Plexus Injury?
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves originating from the spinal cord (C5 to T1) that controls muscle movements and sensations in the arm and hand.
Damage to these nerves can occur due to:
- Road traffic accidents (common in bike accidents)
- Falls or sports injuries
- Birth trauma (Newborn Brachial Plexus Injury)
- Shoulder dislocations or fractures
- Penetrating injuries like knife or gunshot wounds
- Tumors or radiation treatments
- Stretching or tearing forces (Brachial Plexus Avulsion)
When these nerves are stretched, compressed, or torn, the communication between the brain and arm muscles is disrupted, leading to weakness, numbness, or complete paralysis of the arm.
Common Symptoms of Brachial Plexus Injury
Recognizing symptoms early improves treatment outcomes.
Common Brachial Plexus Injury Symptoms include:
- Severe shoulder or arm pain
- Weakness or inability to move the shoulder, elbow, wrist, or fingers
- Loss of sensation or numbness in the arm
- Tingling or electric shock-like sensations
- Muscle wasting (atrophy) over time
- Reduced grip strength
- Complete paralysis of the arm (in severe cases such as Brachial Plexus Avulsion)
If symptoms persist, consult a specialist immediately, as delayed treatment reduces the chances of full recovery.
Types of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Neuropraxia (Stretch Injury)
The nerve is stretched but not torn. Recovery is usually good with rest and physiotherapy.
Nerve Rupture
The nerve is torn but still connected to the spine. Surgery such as nerve grafting is often required.
Brachial Plexus Avulsion
The nerve is pulled away from the spinal cord, causing severe loss of function. Nerve transfer or reconstruction may be needed.
Neuroma
Scar tissue forms around a damaged nerve, causing pain and weakness. Surgical removal or repair may be recommended.
Why Choose Dr. Pradeep Kumar Singh for Brachial Plexus Injury Treatment?
- Highly experienced in complex nerve repair surgeries
- Specializes in brachial plexus surgery and microsurgical nerve reconstruction
- Uses advanced techniques like nerve grafts & nerve transfers
- Personalized care & structured rehabilitation guidance
- Compassionate approach for both adults and infants
- Proven track record of successful recovery outcomes
Dr. Singh ensures that every patient receives individualized treatment designed for functional restoration and long-term health.
Easy Steps of Brachial Plexus Injury Treatment
Diagnosis & Evaluation
A detailed clinical examination, MRI/CT scan, and nerve tests (EMG/NCS) are performed to assess the type and extent of nerve damage.
Individualized Treatment Planning
Based on severity, a customized plan is created — ranging from physiotherapy for mild cases to surgical repair for severe nerve injuries.
Surgical Repair / Reconstruction
When necessary, procedures such as nerve grafting, nerve transfer, or tendon/muscle transfer are performed to restore movement and sensation.
Rehabilitation & Recovery
Post-treatment physiotherapy and guided rehabilitation help rebuild strength, improve mobility, and maximize functional recovery.
Brachial Plexus Injury Treatment Options
Conservative Management
For mild nerve stretch injuries, treatment may include pain medications, arm support, and physiotherapy to maintain movement and prevent stiffness.
Nerve Repair Surgery
If the nerve is torn, direct nerve repair or nerve grafting may be performed to reconnect and restore nerve function.
Nerve Transfer Surgery
When the original nerve cannot recover, a healthy nerve from another area is connected to the affected muscle to restore movement.
Tendon or Muscle Transfer
In severe or long-standing injuries, functional muscle or tendon transfer can help regain essential arm and hand functions.
Rehabilitation & Physiotherapy
Structured physiotherapy is vital after surgery to rebuild strength, improve mobility, and enhance overall recovery.
Recovery Expectations
Recovery depends on:
- Type and degree of nerve damage
- Timing of surgery
- Rehabilitation consistency
- Age and general health of the patient
Some patients recover partial or full movement in:
- 3–6 months (mild injuries)
- 12–24 months (severe reconstruction cases)
Patience and regular physiotherapy play a crucial role.
Schedule Your Consultation Today
If you or your child is experiencing symptoms of brachial plexus injury, do not delay evaluation. Every day counts in nerve recovery. Contact Today for Appointment & Treatment Guidance
Frequently Asked Questions
Can brachial plexus injury heal on its own?
Mild stretch injuries may recover naturally. Severe injuries require surgical repair.
How soon should I consult a brachial plexus specialist?
Immediately. Earlier diagnosis = Better recovery outcomes.
What is the success rate of brachial plexus surgery?
Success depends on severity and timing. Early surgery has a significantly higher rate of movement and strength restoration.
Do newborns with brachial plexus injury always need surgery?
Not always. Many recover with physiotherapy, but persistent weakness after 3–6 months may require surgery.
Is physiotherapy necessary after surgery?
Yes. It is crucial for regaining strength, mobility, and functional movement.
